Organizations are under near-constant cyberattacks and must prepare to respond to any type of incident. One key piece of an effective security operations center (SOC) is having skilled forensic analysts who can quickly identify and mitigate incidents. Here we will discuss the role of forensics in making a SOC ready and explore the benefits of having a dedicated forensics team in your organization. In addition, we will provide tips on getting started in forensics if you want to become a forensic analyst.
How Does Forensic Readiness Help a SOC?
Forensic readiness is critical for any organization that wants to respond effectively to a security incident. A SOC that doesn’t prepare for forensics will likely struggle to collect the necessary data and may even miss important evidence.
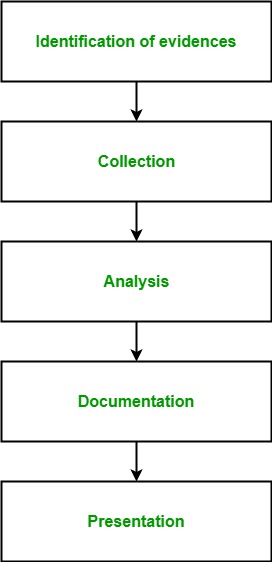
When an incident occurs, the first step is to identify what happened and where. This information then determines the type of forensic analysis needed. The next step is to collect the evidence, which can be challenging, as many organizations do not clearly understand what data needs to be collected. In some cases, organizations are unaware of all the data within their network.
Once the evidence is there, the analysis must begin. This process can be time-consuming and require specialized skills. However, ensuring that the correct information is gathered and following any potential leads is critical.
Organizations should make forensic readiness a priority for their SOC. By doing so, they can ensure that they prepare properly to respond effectively to incidents and collect the necessary data. Doing so will also help to improve the overall security of the organization. (Isaca.org., 2014)
Factors To Consider for Forensic Readiness
Many factors contribute to a strong forensic readiness posture. One of the most important is having a robust incident response plan, which helps an organization rapidly identify, contain, and resolve security incidents. It should also include provisions for collecting and preserving evidence so that professionals can analyze it later.
Another important factor in forensic readiness is the right tools and technologies. This includes hardware and software tools that collect, preserve, and analyze evidence from a security incident. For example, many organizations use digital forensics tools to help them understand what happened during an incident. These tools can examine system logs, network traffic, and other forms of data to reconstruct what occurred.
Finally, having the right people to respond to incidents is also important. This includes having trained staff who are familiar with the organization’s incident response plan and know how to properly use the available tools and technologies. By having the right team in place, an organization can ensure that its response to incidents is swift and effective.
By taking these steps, an organization can be ready to respond quickly and effectively to any security incident.
The Cost and Benefits of Forensic Readiness to An Organization
The benefits of being forensic-ready are numerous. Most importantly, it can help an organization avoid or mitigate reputational damage in the event of a data breach. Additionally, it can help ensure that any legal requirements are met, and that critical evidence is not lost. Furthermore, being prepared can help speed up the forensic investigation process and improve the chances of a successful prosecution if criminal activity occurs.
The cost of being forensic-ready can vary depending on the size and complexity of an organization, but it is typically not overly expensive. The most significant costs are usually associated with setting up the necessary systems and processes and training staff members to use them. However, these upfront costs are typically more than offset by the benefits of being prepared for a digital forensic investigation (Sachowski., 2016).
All organizations should carefully consider the cost and benefits of forensic readiness. While the initial investment is required, the long-term benefits of being prepared far outweigh the costs. Organizations that don’t prepare may find themselves at a significant disadvantage if they ever face a digital forensic investigation.
Forensics is a critical piece in the puzzle of making a SOC ready. By understanding and implementing forensic readiness, you are taking an important step in protecting your organization against cybercrime. The benefits of being forensic-ready far outweigh the costs, so it’s important to consider all factors when deciding.
Source: eccouncil.org