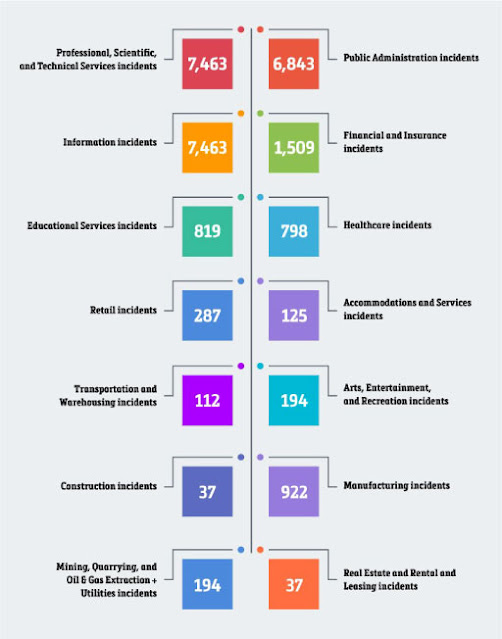
Hackers are the number one threat to modern businesses. That’s according to a survey by PwC, which found that 49% of CEOs are worried about their cybersecurity—more than the number of leaders concerned about the economy (43%) or war (32%) (PwC, 2022).
When you look at cybercrime statistics, you can see why CEOs are so concerned. In 2020, the average business experienced 206 attacks, 22 of which were successful. In 2021, that had risen to 241 attacks per year, of which 29 were successful—a staggering 31% year-on-year rise (Bissell et al., 2022).
Businesses desperately need security personnel at all levels. If you’re an IT professional considering a career change, then a network security job could be the ideal next move.
What Does a Network Security Job Involve?
Network security is about creating systems that allow for the safe movement of data between people and platforms. A network security professional will study the organization’s entire network and try to resolve any vulnerabilities that hackers might exploit.
Network security jobs can range from network security technicians—who are responsible for day-to-day tasks, including reporting and system maintenance—to the architects who design the organization’s network security infrastructure.
The network security team is responsible for tasks such as:
◉ Network security infrastructure management: Working with the security software and hardware that helps fend off cyberthreats. This includes firewalls, antivirus, threat detection systems, and user authentication devices.
◉ Access control: Sensitive data should only be available to those who need it. Network security professionals help implement access control systems that prevent unauthorized data transactions.
◉ Physical security: Hackers can try to use employee devices, or even enter the building and use a terminal. The network security team will help implement physical security measures, including biometric checks.
◉ Data encryption: Encryption reduces the risk of data being intercepted when it moves from point A to point B. Network security will oversee encryption processes to ensure security while also protecting data integrity.
◉ User support: Network security ultimately depends on users following best practices. The network security team will answer questions, provide training materials, and communicate updates about new security measures.
◉ Incident response: In the event of a successful breach, network security will assist in identifying the breach and any associated damage. They will also roll out patches, updates, and other countermeasures to prevent further attacks in the future.
Ultimately, network security is about balancing data safety with data availability. Your role is to help everyone in the organization have access to the systems they need to do their job while ensuring that hackers are kept out.
Is a Network Security Job a Good Career Choice?
Corporate networks are under constant threat, which means they need skilled professionals to help keep them safe. Unfortunately, there is a massive talent gap right now, with up to 3.5 million security jobs going unfilled in 2021 (Morgan, 2022).
This level of demand means there are always plenty of network security jobs available at every level. With cybercrime on the rise, it seems likely that the demand for network security professionals will also increase over time.
Network security professionals often command high salaries. The current national median salaries for related positions include:
◉ Network security system analyst: USD 92,006 (Salary.com, 2022a)
◉ Network security engineer: USD 93,506 (Payscale, 2022)
◉ Network security architect: USD 128,883 (Salary.com, 2022b)
Your long-term career path includes some excellent options, including network security senior architect, or even chief information security officer.
How to Get a Network Security Job Without Prior Experience
Everyone’s got to start somewhere, but how do you get your first network security job?
The good news is that, because of the enormous skills gap, many employers are willing to hire people without prior network security experience. Some companies may provide you with training, support, and on-the-job experience to help you become a security expert.
However, you will need to show that you have the right qualities to succeed in a network security job. Employers will look for someone with strong soft skills, including communication, teamwork, and an analytical approach to thinking.
They will also want to see things like:
IT Background
Employers will want to see that you have experience in an IT role, such as network administration or software development. Ideally, you will have been part of an IT team, and you’ll understand the culture of a network security team.
If you already have a relevant IT certification, you’re in a good position to land a network security job. Relevant certifications include:
◉ Cisco or Microsoft Certified Network Administrator/Engineers
◉ Wireshark Certified Network Analyst
◉ SolarWinds Certified Professional
◉ Juniper Certified Network Professional
◉ Comptia’s Network+/Security+ Certification
All of these are a good foundation for a move into a network security job. Recent graduates might also be able to find network security opportunities if they hold a bachelor’s degree or higher in a relevant discipline.
Interest in Security
Security is a fast-paced world of emerging threats and zero-day vulnerabilities. You have to stay one step ahead of the hackers, and that means studying the latest security news.
If you’re applying for a network security job, you should be able to talk about things like:
◉ Network security fundamentals: At a minimum, you should be able to speak to the core topics of network security. Remember: security is about more than firewalls and antivirus software. There are also organizational issues, such as data availability, and ethical issues, like your responsibilities when handling personal information.
◉ High-profile security incidents: Hackers can make front-page news these days, as in the 2021 Colonial Pipeline attack (Turton, 2021). You should be able to talk about the details of high-profile attacks, including the nature of the exploit and how organizations should respond.
◉ Security thought leaders: There’s a thriving online community of analysts and experts who share advice about network security best practices. It helps to be aware of some prominent blogs, podcasts, and social media accounts that can keep you informed.
A passion for network security can help you stand out as a job candidate, even if you don’t yet have any practical experience.
Relevant Certification
Networking security certifications can show employers that you’re serious about your new career path. A certification training program can also give you a grounding in security concepts so that you’re ready to help protect your new employer from day one.
There are several certifications available, each with a different curriculum. You can search for the one that best suits your needs, but be sure that the course will cover topics like:
◉ Network defense strategies
◉ Network perimeter security
◉ Traffic analysis
◉ Endpoint security
◉ Multiple platforms and operating systems (including Windows, Linux, and macOS)
◉ Cloud security
◉ Virtual networks
◉ Risk management
With a certification from an industry-recognized body, you have a great chance of landing your first network security job.
The Certified Network Defender (C|ND) program from EC-Council is one of the few vendor-neutral network security certifications available. With a C|ND, you’ll have a strong foundation in security principles, plus an unbiased view of security practices. Most importantly, you will have a recognized qualification from an organization that employers know and trust. C|ND is the perfect qualification to get you started in network security jobs like:
◉ Entry-level network administrators
◉ Entry-level network security administrators
◉ Data security analyst
◉ Junior network security engineer
◉ Junior network defense technician
◉ Security analyst
◉ Security operator
Source: eccouncil.org