Defense in depth (DiD) is an information assurance approach where several layers of defense are stationed all through an IT system. It tackles security vulnerabilities in technology, human resources, and operations throughout the system’s life cycle.
DiD derives from a military approach that tries to slow down the progress of an attack, instead of overwhelming it with a robust line of defense, in order to buy more time. The idea of the multi-layered defense approach is that if one approach fails, another would replace it. This increases the network defense of a system and addresses several attack vectors.
Join us as we unpeel the layers of defense in depth and get to the root of why it’s an essential component of a network defense strategy, along with the certifications that you would need as a professional to perform this important role for Employers across the globe.
Why Is Defense in Depth Important?
Today, everything that connects one device to another needs a robust network defense strategy. Understanding and implementing defense in depth is essential, whether you’re a CISO looking to train your employees or cybersecurity professionals seeking new ways to battle old enemies.
Poor network defense practices without a robust defense in depth strategy can lead to businesses suffering malware attacks and phishing cons, leading to damages worth millions and theft of customer data as well as confidential information.
According to IBM, the global average cost of a data breach in 2020 was $3.86 million [1].
As data breaches are set to remain persistent and destructive in the future, the demand for strong network defense and solutions is increasing concurrently.
◉ Businesses can suffer malware attacks, phishing, and human mistakes leading to damages worth millions. Poor network defense practices lead to these issues. Almost every industry sector has been a victim of an attack like this in 2020. Attackers misuse customer data as well as confidential information for their malicious intentions. To ensure that their operations continue with ease, they should always take help from network defense experts.
◉ Professionals need to learn about network defense strategies because it helps raise awareness and improves their online practices. Multiple attacks worldwide have happened because the unaware employees of an organization mistakenly share confidential information with hackers. Through better network security policies, professionals will understand how to avoid such attacks and inform the cybersecurity team before a major incident happens.
◉ Understanding network security practices is also important for students, especially those who are planning to pursue a career in IT or cybersecurity. Initial understanding of network security will help them stay a step ahead during their learning stage as well as in their professional career.
What Are the Key Layers of Defense in Depth?
Administrative controls: These are security essentials that comprise the procedures or policies directed at an organization’s personnel, such as charging users to tag sensitive information as “classified.”
Any control: These controls are directed at an organization’s employees and vendors. Examples include:
◉ Information security policies
◉ Vendor risk management
◉ Third-party risk management frameworks
◉ Cybersecurity risk assessments
◉ Information risk management strategies.
Technical controls: These comprise security essentials that secure network systems or resources through specified hardware or software. Technical controls refer to the software security measures that are installed in the IT infrastructure, such as:
◉ Intrusion protection systems
◉ Web application firewalls
◉ Configuration management
◉ Web scanners
◉ Two-factor authentication
◉ Biometrics
◉ Timed access
◉ Password managers
◉ Virtual private networks
◉ At rest encryption
◉ Hashing
◉ Encrypted backups
Physical controls: These comprise security solutions that block physical access to IT systems. Some of the essential elements of physical controls include:
◉ Locks
◉ Security guards
◉ Surveillance cameras
◉ Keycards
◉ Motion detectors
◉ Demilitarized zones
Network Security Policies
An organization’s network security policy is a document that specifies the security outlooks of the organization. It is an official guideline that mandates users authorized to an organization’s resources, technology, and assets to comply with the laid down rules.
In order to implement a security policy, it is important to outline the precise policy that you intend to implement. Sometimes, these security measures turn out to be exceptionally restricting.
The following policies are enforced by organizations to protect their systems and other critical assets:
◉ Internet access
◉ Device security
◉ Wireless LAN
◉ Remote connection
◉ Intrusion
◉ VPN
◉ Port communication
◉ Firewall rules
◉ DMZ policy
◉ Secure communication policy
◉ Proxy server policy
Network Security Techniques
You need to possess the right techniques and tools to protect your network data from malicious threats and save your organization from destructive losses. Your technique requires you to know how to protect, detect, respond, and predict a broad range of attacks. Defense in depth solutions fall under the protective technique. Key techniques and tools include:
◉ Access control: This allows you to improve your network security by restricting user access and resources to just the sections of the network that clearly relate to the user.
◉ Antimalware and antivirus software: These are network security software created to detect vampiric programs and stop them from spreading.
◉ Anomaly detection: A standard understanding of how networks help you recognize anomalies. You can implement network anomaly detection engines (ADE) to evaluate your network. When you notice an anomaly, you can quickly respond to them.
◉ Application security: This establishes security considerations for critical applications to your network security.
◉ Data loss prevention (DLP): This helps prevent personnel and other users from abusing and potentially compromising valuable data.
◉ Endpoint security: This includes an additional layer of defense between organizational networks and remote devices.
◉ Intrusion prevention systems: IPD/IDS protect the database of known attack vectors so threats can be recognized instantly.
◉ Network segmentation: This helps you give the appropriate access to the appropriate traffic while controlling the traffic from suspicious sources.
◉ Web security: This helps prevent web-based threats such as malicious websites, malicious scripts, or adware programs from leveraging browsers as access points to penetrate a network.
Why Do We Need Hybrid Network Security?
Security threats have progressed from being single attacks to becoming an intricate blend of threats. For instance, Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks are currently introduced by tens of thousands of Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
Even with more traffic being encrypted, security applications still find it hard to detect threats. Cybersecurity professionals and teams are saddled with the overwhelming responsibility to recognize and protect against multifaceted threats.
Hybrid network security includes virtualization, software-defined networking (SDN), and application support across all layers of the service mesh, spanning various hardware devices and data centers. Many applications are applied collectively as a joint solution for defense in depth. It often includes a series of active and passive security applications.
One recognized method of tackling security threats is to construct a visibility fabric through network packet broker (NPB) appliances and virtual agents, alongside network tapping.
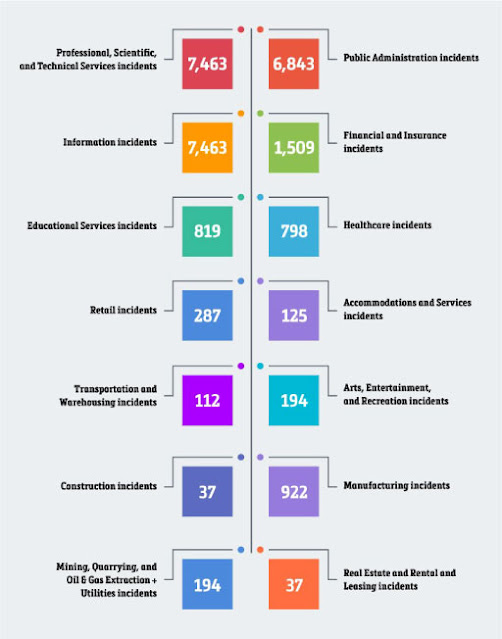
Verizon’s 2020 Data Breach Investigations Report states that 2020 has seen major cyberattacks across different verticals.
The worst-affected sectors were:
Gear Up for the Next Stage of Cyber Defense
Every IT position today requires a certain degree of cybersecurity expertise to protect and defend apps, data, devices, and information. With defense in depth taking its position as the next stage of cyber defense, you need to equip yourself with the latest intel that will prepare you to overcome any challenge. A network security certification course with a dedicated module on defense in depth is your best bet forward, but make sure it aligns with your needs.
Drawing from its vast range of experience, EC-Council’s network security certification courses offer you cutting-edge content that covers everything from defense in depth to threat intelligence. The programs have been designed by a team of industry experts keeping real-world examples in mind. Blue Team Security Certifications like Network Security Fundamentals (NSF) and Certified Network Defender (CND) will provide the right guidance to climb the ladders of success as a cybersecurity expert.
Blue Team Security Certifications
You need security certificates to verify your expertise and improve your employability. Blue Team Security Certifications offer elaborate training in major defensive measures that prove useful for the internal security of modern businesses. Some of the top blue team security certifications include:
Network Security Fundamentals
This one’s for the students and cyber beginners out there! If you want to get a solid grasp of the basics, EC-Council’s Network Security Fundamentals (NSF) course is the way to go. As an entry-level security program, you will get a holistic overview of the vital elements of network security.
Once you’re done with the basics and have decided this is the right career path for you, it’s time to level up with…
Certified Network Defender
If you’re looking to up your network security game, EC-Council’s Certified Network Defender (CND) is the program for you. Not only will it offer you a comprehensive approach to efficiently tackle security issues in today’s modern network, it also maps to the National Initiative of Cybersecurity Education (NICE) and the Department of Defense (DoD) roles for system/network administrators. Rest assured, CISOs can breathe easy knowing their employees are fully equipped to tackle attacks, while students and working professionals will be ready with the job-ready skills they need to fulfill their ambitions.
Source: eccouncil.org