I. Computer or External Hard Disk
If your business is small and limited to a few transactions, you may prefer to save your data on your own computer which is password protected. Of course, this could fill up your computer’s hard drive, so you may have to use an external hard disk. But even though your computer is password-protected and is your personal machine, there are various reasons that may cause loss of data.
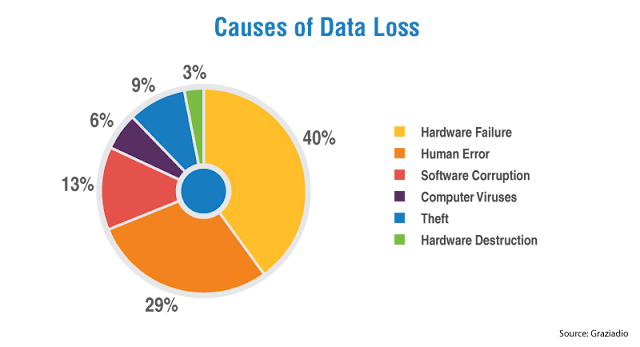
Keeping a backup of your data on any personal computer or hard disk may not be safe, and there is a significant chance that you may lose the data. As the chart above indicates, there is so much risk when all of your data is on one machine. Laptops are frequently lost or corrupted. Of course, there are ways to make your computer a bit more secure.
1) Locking your hard drive with a password: This is one of the easiest options and can be done without any specialized software. This kind of locking is less secure than encryption but still better than no protection. When your computer or laptop gets stolen, the user won’t be able to access the system – at least not without some basic hacking skills. In this way, a password gives some minimal protection to your data. This means that it asks for a password at the initial setup screen and only then will the user be able to access the Windows setup. This kind of password lock is on the hard drive and not on the operating system.
2) Full disk encryption: This is the safest way of keeping your data safe on computer and encryption comes default-enabled on Apple devices. Windows, Linux, and Android users can enable encryption manually. You can also use specialized disk encryption software to lock your device.
II. Server Backup
For larger or more complex businesses, local back-up is not an option. For internal communication, data storage, and backup services, many organizations rely on a server which is well-installed in a separate cabin on the premises of the company. The server should be monitored under a strict surveillance system with uninterrupted power supply. Care must be taken to secure your server because data breaches are a common problem. Over the last year, 83% of organizations surveyed reported data security incidents, which included major vulnerabilities of the security systems and cyber mishaps.
Servers are vulnerable to two major types of threats: internal and external.
Sources of internal threats:
Of all security threats, 58% are attributed to internal threats, and the main sources are employees, ex-employees, and third parties. Sometimes, an employee or contractor knowingly threatens the security of an organization, but many times these incidents are caused by mistake. Problems with employees and contractors can include:
◉ Opening of malicious emails
◉ Getting trapped by phishing schemes
◉ Using corrupted devices
◉ Social engineering
◉ Insufficient vetting of employees and contractors
Sources of external threats:
External threats tend to be people or organizations purposefully attempting to access data that is not their own. These threat actors can include:
◉ Sponsored hackers
These cybercriminals are not money-oriented, but they are information-oriented. All they want is access to your IT infrastructure and (in many cases) your intellectual property (IP). They are sponsored by rival organizations or governments and therefore do not lack the resources required for long-term, sophisticated attacks.
◉ Criminal syndicates
These cybercriminals attack in organized groups and carefully select the targets from where they can get good returns. They tend to be motivated by the money they can earn from selling information they collect illegally.
◉ Hacktivists
These criminals are not motivated by money but instead work for political or social ideologies. One of the most famous hacktivist groups is Anonymous, which is notorious for shutting down websites promoting ideologies they disagree with. Many see them as a force for good instead of evil, but this of course depends on your political and ideological view point.
Combating internal and external threats:
◉ Assess Data Vulnerabilities: Check for vulnerabilities in your system by performing penetration testing and installing IDS (Intrusion Detection System). Also, track all your database access and activities, checking for data leakages, unauthorized access and data transactions.
◉ Calculate risk scores: With the help of a common vulnerability scoring system, you can record vulnerabilities and create a numerical score that can be sorted into low, high, or critical risk to get a broader picture of the threats facing your organization.
◉ Train your employees: It is important that your employees should be aware of the part they play in keeping the system secure. They should be trained on the risks of spam emails, online payments, social engineering, data sharing, introducing unsafe flash drives, and the many other ways they can help or harm the system.
◉ Restrict privileges: Access to sensitive databases should be in accordance with the job function and who is allowed to access what level of data should be reviewed regularly. When an employee leaves the job or changes roles, their access should be immediately removed or changed to ensure that data remains secure.
◉ Encrypt data: Data encryption is a good option for most companies’ data. In this practice, the data is encrypted by mathematical algorithms that are decoded only with authorized access.
3. Cloud Storage
Cloud-based data storage can be more secure than other data storage options when it is configured correctly and strong contracts with service providers are established. When stored in the cloud, the data is first split into chunks, and each chunk is encrypted and stored separately so that if anyone tries to decode the encrypted data, they will be able to access only a part of it if they are successful.
The concept of cloud storage has been developed to provide robust security for databases, but security challenges remain. Cloud security can be strong but no security system is impenetrable. There have been incidents where cybercriminals have hacked cloud systems. Many attempts have been made either to destroy the data or retrieve information from the cloud, and many a times, the hackers were successful too.
According to Microsoft, cyberattacks on the cloud are accelerating every year at a rapid speed. In fact, Microsoft’s Identity Security and Protection team has observed a 300% increase in attacks on cloud services.
How to secure your cloud data:
◉ Use strong authentication: The cloud developers should enable multiple authentications in order to access the data by the cloud owners. Password stealing or change of passwords are common practices for accessing the data from the cloud. A strong authentication policy can curb these practices. Two factor authentication should be employed to secure access to the cloud.
◉ Implement access management: Cloud developers should assign role-based access to the cloud owners to restrict the equal amount of data access to everyone in the company. This way, the most crucial data is only accessible by those who truly need it.
◉ Detect intrusions: Always use an intrusion detection system that can detect and report any malicious activity within the cloud.
◉ Secure APIs and access: Data access should be restricted to only secure APIs by limiting IP addresses or restricting the access to VPNs. If this difficult to implement, then you can secure the data via API using scripts.
Cloud computing technology can be the most secure form of data backup, but due to certain vulnerabilities in the cloud, data can still be quite vulnerable. To safeguard the clouds from cybercriminals, skilled cybersecurity professionals are needed to address specific incidents and situations.
Do you want to be a cybersecurity professional and protect data from cyberattacks? All you need to do is to begin your career path in cybersecurity.
EC-Council has been the world’s leading cybersecurity credentialing body, offering training programs that are mapped to the NICE framework. The industry of cybersecurity is growing as is the need for cyber professionals due to rising cybercrime. This has led to the emergence of specialized job roles including Ethical Hackers, Penetration Testers, Forensic Investigators, and Threat Intelligence Analysts.
Source: eccouncil.org





0 comments:
Post a Comment