Some of the skills that hackers have are programming and computer networking skills. They often use these skills to gain access to systems. The objective of targeting an organization would be to steal sensitive data, disrupt business operations or physically damage computer controlled equipment. Trojans, viruses, and worms can be used to achieve the above-stated objectives.
Read More: 312-50: Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
In this article, we will introduce you to some of the ways that hackers can use Trojans, viruses, and worms to compromise a computer system. We will also look at the countermeasures that can be used to protect against such activities.
What is a Trojan horse?
A Trojan horse is a program that allows the attack to control the user’s computer from a remote location. The program is usually disguised as something that is useful to the user. Once the user has installed the program, it has the ability to install malicious payloads, create backdoors, install other unwanted applications that can be used to compromise the user’s computer, etc.
The list below shows some of the activities that the attacker can perform using a Trojan horse.
◉ Use the user’s computer as part of the Botnet when performing distributed denial of service attacks.
◉ Damage the user’s computer (crashing, blue screen of death, etc.)
◉ Stealing sensitive data such as stored passwords, credit card information, etc.
◉ Modifying files on the user’s computer
◉ Electronic money theft by performing unauthorized money transfer transactions
◉ Log all the keys that a user presses on the keyboard and sending the data to the attacker. This method is used to harvest user ids, passwords, and other sensitive data.
◉ Viewing the users’ screenshot
◉ Downloading browsing history data
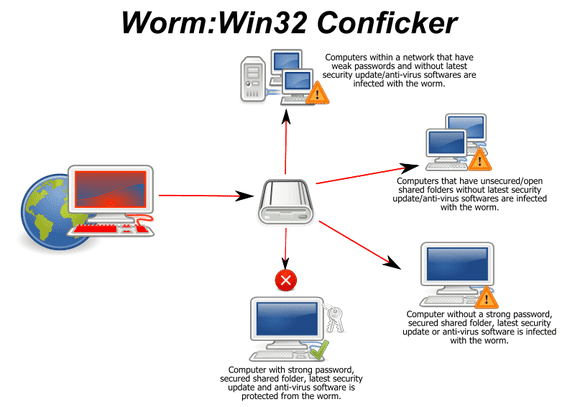
What is a worm?
What is a Virus?
Trojans, Viruses, and Worms counter measures
Trojan, Virus, and Worm Differential Table
| Trojan | Virus | Worm | |
| Definition | Malicious program used to control a victim’s computer from a remote location. | Self replicating program that attaches itself to other programs and files | Illegitimate programs that replicate themselves usually over the network |
| Purpose | Steal sensitive data, spy on the victim’s computer, etc. |
Disrupt normal computer usage, corrupt user data, etc. |
Install backdoors on victim’s computer, slow down the user’s network, etc. |
|
Counter Measures |
Use of anti-virus software, update patches for operating systems, security policy on usage of the internet and external storage media, etc. | ||






0 comments:
Post a Comment